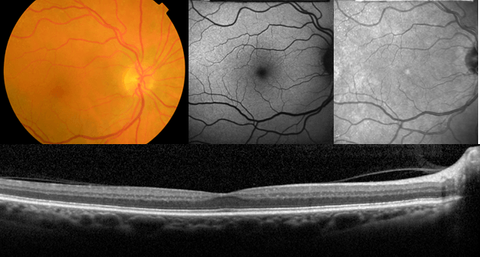
Background
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) remains the leading cause of blindness in the elderly, affecting more than 50 million Europeans. About 15% of affected patients progress to irreversible vision changes and, ultimately, blindness. Therapies to slow progression are becoming available, but clinicians are currently insecure to foresee who will progress and will need swift action to save sight. The identification of biomarkers that can predict AMD progression would help in the implementation of early, targeted treatments and, consequently, in the prevention of vision loss. AMD is a complex disease and latest findings show progression can be predicted by a combination of environmental information, genetics and structural retinal changes. Therefore, heterogeneous patient information, like clinical information, blood samples and in-vivo multimodal imaging of the retina, is acquired and analyzed to extract biomarkers that can be associated with progression risk. However, in contrast to genetic or environmental information, the means to exploit and define biomarkers from imaging are scarcely investigated, although imaging has been proven to provide unique structural information on clinical hallmarks of the disease.
Aim
The goal of this project is to develop automatic tools for discovery of new imaging biomarkers using deep learning that can improve prediction of AMD progression. In this proposal, we aim to develop novel algorithms to combine structural information contained in multimodal and longitudinal retinal images and quantify a rich set of imaging biomarkers that can describe representative disease characteristics correlated with progression. The results will be integrated in a prediction model together with non-imaging biomarkers, such as genetic and environmental markers, to predict the risk of progression to late AMD. This model will give clinicians the possibility to identify patients at high-risk of progression and to provide them active surveillance and personalized therapy to prevent blindness.
Funding
This project is supported by the DCN Radboudumc junior researcher funding scheme.

