This is an AI for Health MSc project. Students are elgible to receive a monthly reimbursement of €500,- for a period of six months. For more information please read the requirements.
Background
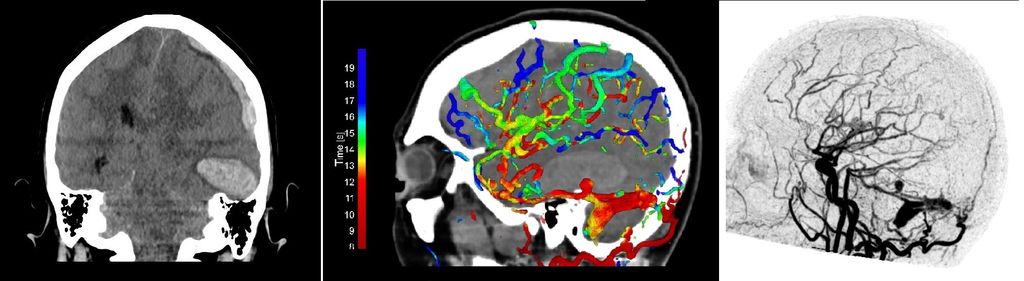
In the diagnostic work-up of patients presenting with an intracranial hemorrhage or pulsatile tinnitus, it can be difficult to detect a possible underlying arteriovenous fistula (AVF). An AVF is an abnormal connection between an artery and a vein. Until recently, an AVF could only be detected with confidence based on invasive conventional angiography. Drawbacks of conventional angiography are the relatively time-consuming procedure, high cost, radiation exposure for both patient and operator, and a risk of transient or permanent neurologic complications. Dynamic CTA, also referred to as 4D-CTA, is a new imaging modality which enables the noninvasive evaluation of intracranial vasculature hemodynamics by multiple subsequent CT acquisitions over a period of time. However, the high spatial and temporal resolution of 4D-CTA yields large amounts of data resulting in laborious and time-consuming diagnostic evaluation and hampers direct interpretation, even for experienced observers. Computer aided diagnosis would therefore be beneficial for the detection and evaluation of cranial AVFs. The aim of this project is to develop AI for labeling of the intracranial vessel segments including AVFs on 4D-CTA. Labeling is not only important for the automated detection of AVFs and potentially other abnormalities such as vascular occlusions, but also facilitates human interpretation of the results that are found by the computer.
Material and Methods
This project builds upon previous work at our department. In previous work, we have developed a deep learning algorithm for robust segmentation of the complete cerebral vasculature and for artery-vein separation in 4D-CTA.
Tasks
- Collecting and labeling of 4D-CTA of patients with and without shunt
- Development of AI for detection of arteriovenous shunts
- Development of a demonstrator
- Writing of manuscript in accordance with publication guidelines
Innovation
The developed tool will be tested and subsequently implemented in the department of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine of the Radboudumc.
Requirements
- Students with a major in artificial intelligence, computer science, engineering, physics or related area and in their final stage of a master level studies are invited to apply
- Interest in medical image analysis
- Affinity with programming Python and with deep learning packages (e.g. PyTorch) is required
Information
- Project duration: 6 months
- Location: Radboud University Medical Center
- For more information, please contact Anton Meijer


